What is methanol or methyl alcohol?
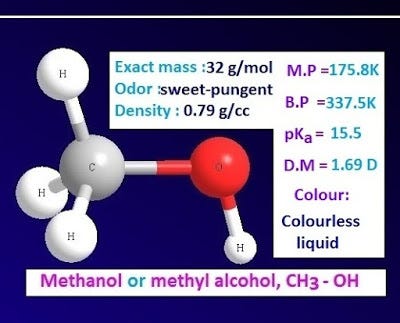
Methanol is a monohydric alcohol of alcohol family. It is the simplest alcohol. Methanol is also known as methyl alcohol or carbinol with chemical formula CH3-OH.
The other names of methanol are hydroxymethane, methylol, wood spirit, wood naphtha, methylene hydrate, pyroligneous spirit etc.
The carbon atom of methanol is attached with three hydrogen atom and one hydroxyl group (-OH) directly.
Methanol is a colorless, sweet and pungent smelling, inflammable liquid. It is poisonousliquid. Melting point of methanol is — 97.8ᵒC and the boiling point is 64.5ᵒC.
Methanol is miscible with water in all proportions due to formation of hydrogen bond and it is also soluble in organic solvents.
It burns with a faintly luminous flame and its vapor forms explosive mixtures with air or oxygen when ignited.
Methanol combines with calcium chloride to form CaCl2.4CH3-OH and hence can’t be dried this way.
Read more : What is hydrolysis reaction in organic chemistry?
Read also : What is urea fertilizer in chemistry?
Methanol structure and chemical formula
Different analysis and molecular weight determinations show that the chemical formula of methanol is CH4O or CH3OH.
Assuming the carbon atom is tetra valent, oxygen bivalent and hydrogen univalent, only one structure of methanol, CH3OH is possible.
This is supported by all the chemical reactions of methanol. For example, one H-atom in methanol is replaced by Na, which indicates that one H-atom is in a different state of combination from the other three.

Again, methanol is formed from CH3-Cl by hydrolysis with NaOH. Now CH3-Cl can have only the structure CH3-Cl.
It is reasonable to suppose that the -CH3 group in CH3-Cl remain unchanged in reaction with dilute NaOH.
This means that the reaction takes place by the replacement of the ‘Cl’-atom by a — OH group.
The presence of — OH group is confirmed by the reaction between methanol and PCl5. This is also supported by I.R and NMR spectroscopy studies.
In methanol, both carbon atom and oxygen atom are sp3 hybridized. The structure of methanol with H — O — C bond angle is shown below.
Methanol molar mass and density
The chemical or molecular formula of methanol is CH4O or CH3-OH. The exact molar mass of methanol is 32.04.
Methanol is a colorless liquid due to formation of intra molecular hydrogen bond. The density of methanol is 0.79 g/cc.
Preparation or synthesis of methanol
Methanol is an important alcohol. A large amount of methanol is used in different industrial sector. So a large scale methanol is required.
There are several methods for preparation of methanol industrially. But the most important methods for synthesis of methanol from water gas.
It is very important synthetic process. Most amount of methanol is synthesized in this method.
In this method, methanol vapor is produced when a mixture of equal volumes of water gas and hydrogen gas is passed on copper oxide, zinc oxide and chromium oxide (CuO + ZnO + Cr2O3) catalyst.
The catalyst is heated at 300–400ᵒC temperature under 200–300 atmospheric pressure. 99% methanol is obtained by cooling this methanol vapor.
(CO + H2) + H2 ⟶ CH3-OH (methanol)
How to prepare methanol from CO2?
There is no direct method for preparation methanol from CO2. But methanol can be prepared from CO2 indirectly in several steps.
In first step, CO2 reacts with Grignard reagent (CH3-Mg-Br) followed by hydrolysis gives acetic acid. This acetic acid forms methane on heating with sodalime (CaO + NaOH).
Finally, methanol is obtained by passing a mixture of methane and oxygen through a Cu-tube under 100 atmosphere pressure and 200–250ᵒC temperature.

In other method, silver salt of acetic acid reacts with bromine in presence of CCl4 resulting in the formation of CH3-Br, which on hydrolysis gives methanol.
Methanol boiling point explanation
The boiling point of methanol is 64.5ᵒC, which is higher than that of alkane and ether compounds.
This is because of methanol contains polar O — H bond and hence it can form intra-molecular hydrogen bond.
So a large amount of heat energy is required to break this huge number of hydrogen bond.
Consequently, the boiling point of methanol is higher than other compounds with equivalent molecular weight.
Is Methanol Poisonous?
Methanol is a very poisonous liquid. Drinking of methanol can lead to blindness, mad or even death.
Methanol is toxic by two mechanisms. First, methanol can be fatal due to effects on the central nervous system, acting as a central nervous system depressant like ethanol poisoning.
Second, in a process of toxication, it is metabolised to formic acid via formaldehyde in a process initiated by the enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase in the liver. So it is not used as an alcoholic beverage.
Depending on its toxic properties, methanol is frequently used as a denaturant additive for ethanol made for industrial uses.
This addition of methanol exempts industrial ethanol (commonly known as ‘denatured alcohol’ or ‘methylated spirit’) from liquor excise taxation in different countries.
Methanol uses
Methanol is a very important organic alcohol. It has a large application in industrial sectors and also many other purpose.
· Methanol is widely used in industry as a cheap solvent for store-room, paints, varnishes, celluloid, cement, fats, etc.
· HCHO is a very important raw material in the plastics industry. Methanol is used extensively in the production of these HCHO.
· Methanol is used as an alternative to petrol in countries around the world where motor vehicle fuel is low. Methanol is also used as a fuel when mixed with petrol.
· In temperate countries, a mixture of water and methanol is used as an antifreeze liquid instead of water in automobile radiators.
· Methanol is added to ethyl alcohol to make it inedible. Ethyl alcohol containing 10% methanol is called methylated spirit.
Others application
Methanol is used in the manufacturing of dyes, perfumes, etc. It is also used in the preparation of methane, methyl halides, methyl acetate ester, formic acid, carbon dioxide, etc.
