MnO2 oxidation reaction with example
MnO2 oxidation introduction
MnO2 oxidation reaction is essential both in organic as well as in inorganic chemistry. MnO2 oxidation process is especially used for organic synthesis.
MnO2 is an inorganic chemical compound. It is also known as manganese (IV) oxide.

MnO2 oxidation number
The oxidation number of Mn in MnO2 is +4. But the highest and lowest oxidation number of Mn atom may be +7 and -1 respectively.
Therefore, Mn atom in MnO2 can increase and also decrease its oxidation number from +4 to +7 or +4 to 0, -1.
Consequently MnO2 behave as a strong oxidizing agent and commonly used in the oxidation organic compounds.
MnO2 oxidation reaction examples
A specialized use of manganese dioxide is as oxidant in organic synthesis.
There are few organic reactions where MnO2 is used as an oxidizing agent.
Such as, allyl alcohol and benzyl alcohol are oxidized by active MnO2 to form α, β-unsaturated aldehyde. The reaction takes place in the presence of inert solvent CH2Cl2 or CCl4.
MnO2 oxidizes allylic alcohols to the corresponding aldehydes or ketones. In this case the configuration of the double bond remains unchanged.
The corresponding acetylenic alcohols are also suitable substrates, although the resulting propargylic aldehydes can be quite reactive.
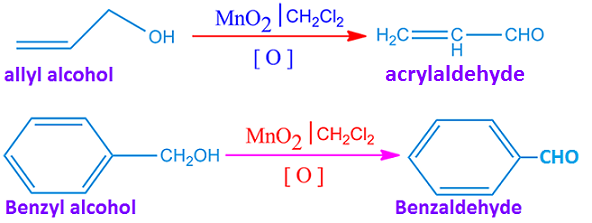
MnO2 oxidation process is also applied for converting of toluene to benzaldehyde in presence of oxygen molecule. Besides, 1, 2-diols are cleaved by MnO2 to dialdehydes or diketones.
The reaction is carried out in the presence of inert gas (nitrogen) under 500ᵒC temperature.

Again some inorganic substances also oxidized by MnO2. Such as hot concentrated HCl acid concentrated sulfuric acid are oxidized by MnO2 to release Cl2, O2 respectively.
MnO2 also oxidize coke to CO. For this reason MnO2 oxidation is applied in steel industry.

